What is aurora?
The aurora is displayed when the solar wind strikes atoms in the magnetosphere. The disturbance will cause the electrons in the atoms and move to a higher-energy level once the electrons drop back to the lower level it will cause a fantastic light on the sky, and that’s how aurora borealis is created.
How to see the Northern Lights?
After the scientific introduction, let's talk about the different factors that you will have to look at to be able to see Northern Lights, and all of them together give you a chance to see it during your chasing night. With hello aurora app, you will have all these explanations within the app along with other fun features to help you see the aurora easier!
- Read more about how to take pictures of the Northern Lights.
- Read the ultimate guide to aurora hunting for beginner.
Strength
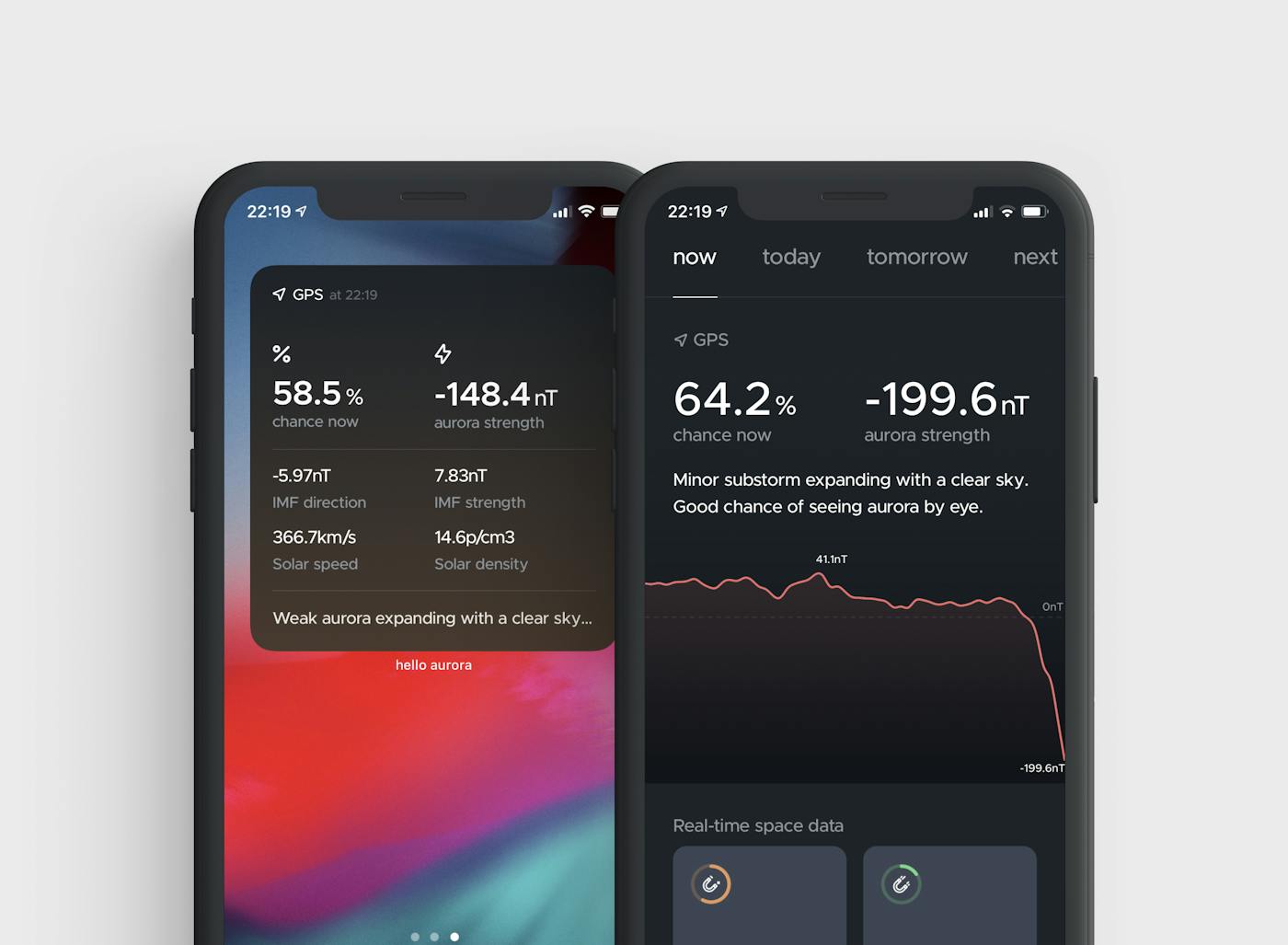
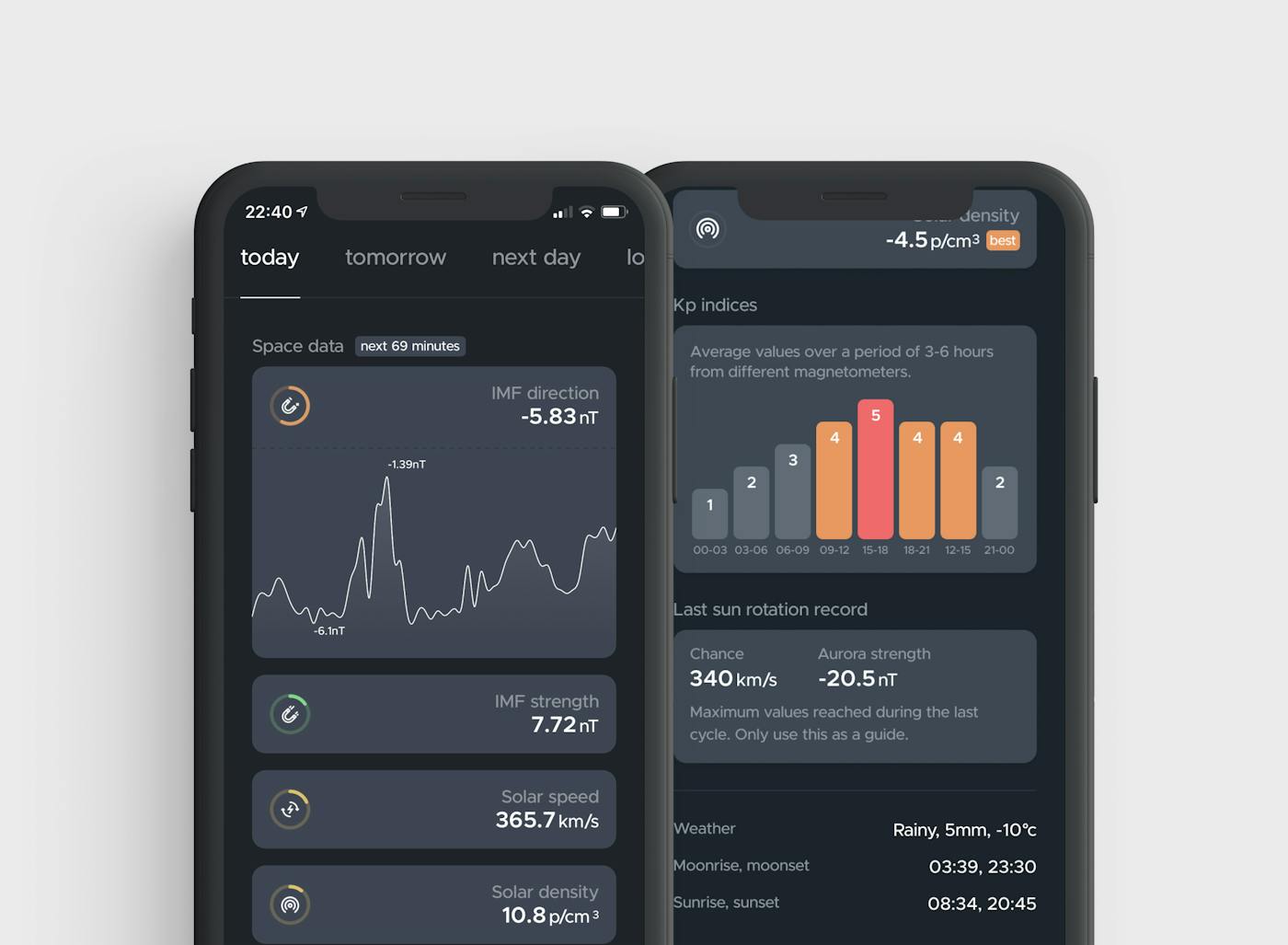
In March 2020, we started using real-time data coming from magnetometers and provided with the help of multiple spatial agencies around the North Pole. A magnetometer is a device that measures the fluctuation of the aurora in the Earth's magnetic field.
When the value measured is dropping quickly in the negative (~-150nT), it means an aurora has a high chance to be dancing in the sky, and is called a substorm. The lowest it gets, the stronger the aurora will be. We are then talking about magnetic storms.
When in the opposite the value is growing a lot, it can mean the aurora is charging (~150nT) and will release with a display in the next few minutes or will come back to an average value (~5nT) until the next fluctuation.